Abstract
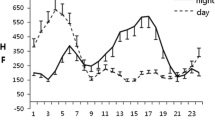
Object: The purpose of this study was to compare the stress levels of Japanese ambulance men between on-duty and off-duty days, by using the physiological indices of heart rate variability (HRV) and cortisol in urine, measured over each 24-h period. Methods: Measurements were made during one on-duty and one off-duty day for each subject. The participants were monitored for 24 h with a Holter recording system and a parameter reflecting overall stress levels was obtained by measuring the cortisol level in urine collected over 24 h. Results: The circadian variation of cardiac autonomic nervous system activity was affected when the subjects were on duty. The low-frequency/high-frequency power ratio (=low-frequency power/high-frequency power: LF/HF), which is a useful parameter that reflects the balance of cardiac autonomic nervous activity, differed significantly between the waking and sleeping times on the off-duty day (P=0.03), while it did not differ between these two states on the on-duty day (P=0.56). Similarly, the normalized high-frequency power [=high-frequency/(high-frequency+low-frequency) power: HF/(HF+LF)] ratio, which is a useful measure of the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, differed significantly between these two states on the off-duty day (P=0.04), while there was no significant difference in the ratio between the two states on the on-duty day (P=0.13). Conclusion: These results show that the diurnal balance of the cardiac autonomic nervous system is affected on the on-duty day, even though it is possible for ambulance men to sleep regular hours.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera G (1994) Regulation of pituitary ACTH secretion during chronic stress. Front Neuroendocrinol 15:321–350
van Amelsvoort LG, Schouten EG, Maan AC, Swenne CA, Kok FJ (2000) Occupational determinants of heart rate variability. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 73:255–262
Baselli G, Cerutti S, Civardi S, Liberati D, Lombardi F, Malliani A, Pagani M (1986) Spectral and cross-spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial blood pressure variability signals. Comput Biomed Res 19:520–534
Bernardi L, Ricordi L, Lazzari P, Solda P, Calciati A, Ferrari MR, Vandea I, Finardi G, Fratino P (1992) Impaired circadian modulation of sympathovagal activity in diabetes. Circulation 86:1443–1452
Cohen H, Kotler M, Matar MA, Kaplan Z, Miodownik H, Cassuto Y (1997) Power spectral analysis of heart rate variability in posttraumatic stress disorder patients. Biol Psychiatry 41:627–629
Cohen H, Kotler M, Matar MA, Kaplan Z, Loewenthal U, Miodownik H, Cassuto Y (1998) Analysis of heart rate variability in posttraumatic stress disorder patients in response to a trauma-related reminder. Biol Psychiatry 44:1054–1059
Dishman RK, Nakamura Y, Garcia ME, Thompson RW, Dunn AL, Blair SN (2000) Heart rate variability, trait anxiety, and perceived stress among physically fit men and women. Int J Psychophysiol 37:121–133
Eckberg DL, Drabinsky M, Braunwald E (1971) Defective cardiac parasympathetic control in patients with heart disease. N Engl J Med 285:877–883
Fujita M, Miyamoto S, Sekiguchi H, Eiho S, Sasayama S (2000) Effects of posture on sympathetic nervous modulation in patients with chronic heart failure. Lancet 356:1822–1823
Furlan R, Guzzetti S, Crivellaro W, Dassi S, Tinelli M, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Lombardi F, Pagani M, Malliani A (1990) Continuous 24-hour assessment of the neural regulation of systemic arterial pressure and R-R variabilities in ambulant subjects. Circulation 81:537–547
Furlan R, Piazza S, Dell’Orto S, Barbic F, Bianchi A, Mainardi L, Cerutti S, Pagani M, Malliani A (1998) Cardiac autonomic patterns preceding occasional vasogal reactions in healthy humans. Circulation 98:1756–1761
Furlan R, Barbic F, Piazza S, Tinelli M, Seghizzi P, Malliani A (2000) Modifications of cardiac autonomic profile associated with a shift schedule of work. Circulation 102:1912–1916
Goldstein IB, Jamner LD, Shapiro D (1992) Ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate in health male paramedics during a workday and a nonworkday. Health Psychol 11:48–54
Gronfier C, Simon C, Piquard F, Ehrhart J, Brandenberger G (1999) Neuroendocrine processes underlying sleep regulation in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:2686–2690
Guzzetti S, Dassi S, Pecis M, Casati R, Masu AM, Longoni P, Tinelli M, Cerutti S, Pagani M, Malliani A (1991) Altered pattern of circadian neural control of heart period in mild hypertension. J Hypertens 9:831–838
Janszky I, Ericson M, Mittleman MA, Wamala S, Al-Khalili F, Schenck-Gustafsson K, Orth-Gomer K (2004) Heart rate variability in long-term risk assessment in middle-aged women with coronary heart disease: The Stockholm female coronary risk study. J Intern Med 255:13–21
Karlsson BH, Knutsson AK, Lindahl BO, Alfredsson LS (2003) Metabolic disturbance in male workers with rotating three-shift work. Results of the WOLF study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 76:424–430
Kobayashi F, Furui H, Akamatsu Y, Watanabe T, Horibe H (1997) Changes in psychophysiological functions during night shift in nurses: Influence of changing from a full-day to a half-day work shift before night duty. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 69:83–90
Koizumi K, Terui N, Kollai M (1985) Effect of cardiac vagal and sympathetic nerve activity on heart rhythmic fluctuations. J Auton Nerv Syst 12:251–259
Lio D, Carnethon M, Evans GW, Cascio WE, Heiss G (2002) Lower heart rate variability is associated with the development of coronary heart disease in individuals with diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Diabetes 51:3524–3531
Lombardi F, Sandrone G, Pernpruner S, Sala R, Garimoldi M, Cerutti S, Baselli G, Pagani M, Malliani A (1987) Heart rate variability as an index of sympathovagal interaction after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 60:1239–1245
Lombardi F, Sandrone G, Mortara A, La Rovere MT, Colombo E, Guzzetti S, Malliani A (1992) Circadian variation of spectral indices of heart rate variability after myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 123:1521–1529
Matthews KA, Gump BB, Owens JF (2001) Chronic stress influences cardiovascular and neuroendocrine responses during acute stress and recovery, especially in men. Health Physiol 20:403–410
Miyamoto S, Fujita M, Tambara K, Sekiguchi H, Eiho S, Hasegawa K, Tamaki S (2004) Circadian variation of cardiac autonomic nervous activity is well preserved in patients with mild to moderate chronic heart failure: effect of patient position. Int J Cardiol 93:247–252
Molgaard H, Sorensen KE, Bjerregaard P (1991) Circadian variation and influence of risk factors on heart rate variability in healthy subjects. Am J Cardiol 68:777–784
Montano N, Cogliati C, Porta A, Pagani M, Malliani A, Narkiewicz K, Abboud FM, Birkett C, Somers VK (1998) Central vagotonic effects of atropine modulate spectral oscillations of sympathetic nerve activity. Circulation 98:1394–1399
Pagani M, Lombardi F, Guzzetti S, Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Pizzinelli P, Sandrone G, Malfatto G, Dell’Orto S, Piccaluga E (1986) Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog. Circ Res 59:178–193
Parati G, Castiglioni P, Di Rienzo M, Omboni S, Pedotti A, Mancia G (1990) Sequential spectral analysis of 24-hour blood pressure and pulse interval in humans. Hypertension 16:414–421
Petelenz M, Gonciarz M, Macfarlane P, Rudner R, Kawecki P, Musialik J, Jalowiecki P, Gonciarz Z (2004) Sympathovagal balance fluctuates during colonoscopy. Endoscopy 36:508–514
Peter R, Alfredsson L, Siegrist J, Westerholm P (1999) Does a stressful psychosocial environment mediate the effects of shift work on cardiovascular risk factors? Scand J Work Environ Health 25:376–381
Pomeranz B, Macaulay RJ, Caudill MA, Kutz I, Adam D, Gordon D, Kilborn KM, Barger AC, Shannon DC, Cohen RJ, Benson H (1985) Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis. Am J Physiol 248:151–153
Rimoldi O, Pierini S, Ferrari A, Cerutti S, Pagani M, Malliani A (1990) Analysis of short-term oscillations of R–R and arterial pressure in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 258:H967–H976
Sayers BM (1973) Analysis of heart rate variability. Ergonomics 16:17–32
Smith L, Folkard S, Poole CJM (1994) Increased injuries on night shift. Lancet 344:1137–1139
Yehuda R, Halligan SL, Yang RK, Guo LS, Makotkine I, Singh B, Pickholtz D (2003) Relationship between 24-hour urinary-free cortisol excretion and salivary cortisol levels sampled from awakening to bedtime in healthy subjects. Life Sci 73:349–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitani, S., Fujita, M. & Shirakawa, T. Circadian variation of cardiac autonomic nervous profile is affected in Japanese ambulance men with a working system of 24-h shifts. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 79, 27–32 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-005-0026-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-005-0026-y