Summary
A serum concentration profile study on midazolam in children was done. Fifty six children aged 3–10 years took part. The routes investigated were intravenous, intramuscular, rectal and oral at 0.15 mg·kg−1, and the oral at 0.45 mg·kg−1 and 1 mg·kg−1. Serum concentration levels for 5 h were studied using gas liquid chromatography.
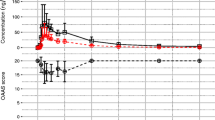
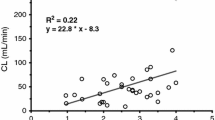
The volume of distribution, Vss, was 1.29 l·kg−1, the elimination half-life 1.17 h and the serum clearance 9.11 ml·kg−1·min−1. Peak serum concentrations for the intramuscular, rectal and oral routes were at 15 min, 30 min and 53 min respectively. Bioavailability was 87%, 18%, 27% respectively at a dose of 0.15 mg·kg−1. The oral route bioavailability halved to 15% at the two higher doses.
Bioequivalence was present between the 0.15 mg·kg−1 intramuscular dose and the 0.45 mg·kg−1 oral dose from 45 to 120 min.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenblatt DJ, Lochniskar A, Ochs RH, Lauven PM (1981) Automated gas chromatography for studies of midazolam pharmacokinetics. Anesthesiology 55: 176–179
Dundee JW, Samuel IO, Toner W, Howard PJ (1980) Midazolam a water soluble benzodiazepine. Anaesthesia 35: 454–459
Reves JG, Frazen RJ, Vinik H, Greenblatt DJ (1985) Midazolam, pharmacology and uses. Anesthesiology 62: 310–324
Greenblatt DJ, Arendt RM, Abernathy DR, Giles HG (1983) In vitro quantiation of benzodiazepine lipophilicity. Br J Anaesth 55: 985–989
Whitwam JG (1987) Benzodiazepines — editorial. Anaesthesia 42: 1255–1257
Crevoisier C, Ziegler WH, Eckart M, Heijmann P (1983) Relationship between plasma concentration and effect of midazolam after oral and intravenous administration. Br J Clin Pharmacol 16: 51–61
Crevoisier C, Eckert M, Heijmann P, Thurneysen D (1981) Relation entre 1 effect clinique et al pharmacocinetique due midazolam après 1 administration IV et IM. Arzneimittelforsch 31: 2211–2215
Rita L, Seleny FL, Majurek A, Robins S (1985) Intramuscular midazolam for paediatric premedication sedation. Anesthesiology 63: 528–531
Payne KA, Heydenrych JJ, Kruger TC, Samuels G (1986) Midazolam premedication in paediatric anaesthesia. South Afr Med J 70: 657–659
Corman HH, Hornick EJ, Kritchman M, Terestman N (1958) Emotional reactions of surgical patients to hospitalization, anaesthesia and surgery. Am J Surg 21: 330–337
Padfield NL, Twohig M, Frazer AC (1986) Temazepam and trimeprazine compared with placebo as premedication in children. Br J Anaesth 58: 487–493
White PF (1986) Pharmacologic and clinical aspects of preoperative medication. Anesth Analg 65: 963–974
Fee JPH (1988) Premedication. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 32: 1–5
Kretz FJ, Liegl M, Heinemeyer G, Eyrich K (1985) Die rektale Narkoseeinleitung bei Kleinkindern mit Diazepam und Midazolam. Anästhesiol Intensivmed 10: 343–346
Saint-Maurice C, Meistelman C, Rey E, Estene C, De Louture D, Olive G (1986) The pharmacokinetics of rectal midazolam for premedication in children. Anesthesiology 65: 536–538
Brown TCK, Fisk GC (1979) Preoperative preparation including premedication. In: Anaesthesia for children. Brown TCK, Fisk GC (eds) Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 103–108
De Roubaix JAM (1985) Premedikasie feite en fiksie. South Afr J Cont Med Educ 3: 7–19
Haagensen RE (1985) Rectal premedication in children. Anaesthesia 40: 956–959
Cote C, Goudsouzian NG, Letty M, Lin MD, Dedrick C (1982) Assessment of the risk factors related to acid aspiration syndrome in paediatric patients. Anesthesiology 56: 70–72
Yildiz F, Tryba M, Kuehn K, Hausdoerfer J (1984) Reduction in gastric acid secretion. Anaesthesia 39: 314–318
Harper KW, Collier PS, Dundee JW, Elliott P, Halliday NJ, Lowry KG (1985) Age and nature of operation on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam. Br J Anaesth 57: 866–871
Lloyd Thomas AR, Booker PD (1986) Infusion of midazolam in paediatrics after cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 58: 1109–1115
Payne KA, Heydenrych JJ, Martins M, Samuels G (1987) Caudal block for analgesia after paediatric inguinal surgery. South Afr Med J 72: 629–630
Nimmo WS (1984) Effect of anaesthesia on gastric motility and emptying. Br J Anaesth 56: 29–36
Nimmo WS, Heading RC, Wilson J, Tothill P, Prescott L (1975) Inhibition of gastric emptying and drug absorption by narcotic analgesics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2: 509–513
Kanto J, Aaltonen L, Himberg J (1986) Midazolam as an intravenous induction agent in the elderly. Anesth Analg 65: 15–20
Benet LZ, Galeazzi RL (1979) Non-compartmental determination of the steady state volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci 68: 1071–1074
Gibaldi M (1984) Non-compartmental pharmacokinetics. In: Gibaldi M (ed) Biopharmaceutics and clinical pharmacokinetics, 3rd edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 17–28
Metzler CM (1974) Bioavailability — a problem of equivalence. Biometrics 30: 309–317
Westlake WJ (1975) Statistical problems in interpreting comparative bioavailability trials. Int J Clin Pharmacol 11: 342–345
Langman MJS (1986) Towards estimation and confidence intervals. Br Med J 292: 716
Gardner MJ, Altman DG (1986) Confidence intervals rather than P values. Br Med J 292: 746–750
Rothman KJ (1978) A show of confidence. N Engl J Med 14: 1362–1363
Persson P, Nilsson A, Hartvig P, Tamsen A (1987) Pharmacokinetics of midazolam in total IV anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 58: 548–556
Hull CJ (1984) General principles of pharmacokinetics. In: Prys-Roberts C, Hug CC (eds) Pharmacokinetics of anaesthesia. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 1–24
Schwilden H, Stoeckel H, Schuttler J, Lauven P (1986) Pharmacological models and their use in clinical anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol 3: 175–208
Greenblatt DJ, Abernethy DR, Lochniskar A, Harmatz J, Limjuco RA, Shader RI (1984) Affects of age, gender and obesity on midazolam kinetics. Anesthesiology 61: 27–35
Harper KW, Collier PS, Dundee JW, Elliott P, Holliday NJ, Lowry KG (1985) Age and natuare of operation influence the pharmacokinetics of midazolam. Br J Anaesth 40: 956–559
Aaltonen L, Himberg J, Kanto J, Vuori A (1985) The usefulness of gas liquid chromatography in pharmacokinetic studies on midazolam. Int J Clin Pharmacol 23: 247–252
Greenblatt DJ, Lochniskor A, Scavone M (1986) Absence of interaction of cimetidine and ranitidine with intravenous and oral midazolam. Anesth Analg 65: 176–180
Bornemann LD, Min BH, Crews T, Rees MM (1985) Dose dependant pharmacokinetics of midazolam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 91–95
Gerecke M (1983) Chemical structure and properties of midazolam. Br J Clin Pharmacol 16: 11–16
Reinhart K, Dallinger G, Dennhardt R, Heinemeyer G, Eyrich K (1985) Comparison of midazolam, diazepam and placebo as I.M. premedication. Br J Anaesth 57: 294–299
Ziegler WH, Schalch E, Leishman B, Eckert I (1983) Comparison of the effects of IV administration of midazolam and the hydroxy metabolites. Br J Clin Pharmacol 16: 635–695
Kanto J (1983) Midazolam, the first water soluble benzodiazepine derivative. Drugs Today 19: 221–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Addendum: This manuscript is part of a research project submitted to the Medical School of the University of Stellenbosch, South Africa, in support of a M.D. thesis. The promotor is Prof. A.R. Coetzee M. Med., F.F.A.(S.A.), FFARCS(I), Ph.D., M.D.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Payne, K., Mattheyse, F.J., Liebenberg, D. et al. The pharmacokinetics of midazolam in paediatric patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 37, 267–272 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00679782
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00679782